The license used for MoBlo articles is CC BY-ND 4.0
5. Business Transactions (BT)
Previous parts of this document have an architecture approach. They give elements to determinate the population, the software architecture and the data architecture. This part gives a point of view more business-related.
This part presents the transactions that will make sense in the BlockChain. Assuming that the technical part of a transaction is valid, a transaction carries data in the BlockChain that can be used in non-currency use case, then the transaction has to be coherent.
5.1. Modelization
Each transaction has an origin and a destination. Each transaction carries more or less data.

Figure 5-1 - BT - Simple Transaction
In the represented transaction, Alice sends to Bob units of the Asset Aj with a complement of data dk using the transaction ti.

Figure 5-2 - BT - MultiSig Transaction
In the case of MultiSign Addresses, origin can be easily specified. Here Alice and Bob send to Carol, 10 units of A5 and 6 units of A12 by the transaction tz.
The identification of transaction takes importance when the sense comes from successive transactions, then triggers can be identified.
5.2. Library use case BT
The Library use case presents a lot of possible transactions.

Figure 5-3 - BT - Library - Sign Up
Readers use a Web Gate to access to the Information System. Then, when a new Reader wants to sign up, he uses the Web Gate. Here the arrow is dotted to indicate that it is not a BlockChain transaction. The modelization of such a transaction can be useful to completely describe the use case and remind the importance of the Web Gate.

Figure 5-4 - BT - Library - Distribution
The Central Library creates the Assets and the units of Asset. When, in the real life, the book is sent to a Library (L), the Central Library (CL) has to send a unit of the Asset to the Library.

Figure 5-5 - BT - Library - Centralisation
Books can be returned in any library. Then a library can stored many copies of the same book. The books have to be sent to the Central Library.
The booking of a particular book can be a reason too. A book is available in only one copy. If someone wants to read it, the book has to be transferred from a Library to another one passing by Central Library.
Anyway, the BlockChain indicates where the available books are located.

Figure 5-6 - BT - Library - Loaning
A Reader (R) can borrow a book. The book is then taken from a Library (Central Library or other Library) and sent to the Reader. The transaction can carry the End Date of the loan.

Figure 5-7 - BT - Library - Return
The simple cycle of book can be ended with the case of the return. A Reader returns a book, and the unit is sent back to the Library.
At this point, the system is a ledger which allows to know where a book is located.
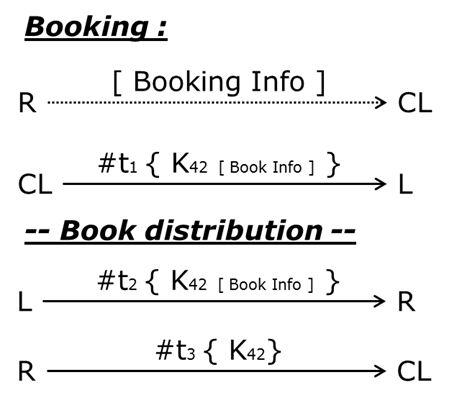
Figure 5-8 - BT - Library - Booking
Here is a sequential use case, where transactions have a related number to indicate the order which has to be followed.
The Booking allows the Readers to ask for a specific book in a specific library. Remind that Readers can only use the Web Gate and only the Central Library can create Assets and Asset units.
The Reader (R) asks for a book using the Web Gate. One unit of the Asset Booking (K) is sent from the Central Library to the destination Library (L) asked by the Reader. The transaction carries on information about the Booking (book reference, destination library …)
Now the system knows that the book is waited in a particular Library. The first case is “The book is already in the library”, and then there is nothing to do. The second case is “The book is only available in another library” and then batches take care to return the book to Central Library and then distribute it to the destination Library.
When the book is available in the destination library, this Library sends the unit of Booking to the Reader to notify him that the book is waiting for him in the Library. At the end, when the Reader comes to loan the book, the unit of Booking is returned to Central Library.
Notice that the first step of Booking is done after using Web Gate. A business part has to be implemented. In this part, a rule can specify how many Bookings can be done by the same Reader at the same time. But, this rule doesn’t appear in this BlockChain modelization.

Figure 5-9 - BT - Library - Delay
The last part of the use case is the Delay in book return. Transactions are created by the batches which are using the Central Library address based on loaning information. When a book is loaned, the end date is specified, the system easily allows to find Books loaned by Readers out of End Date.
In this case, one unit of Delay is sent to the Reader (R) from the Central Library (CL) with a reference on the book out of date.
When the Reader returns the book, he sends to the Library the unit of Book and the unit of Delay.
5.3. Forum use case BT
Forum is a simplest use case limited to two cases: open a new subject and comment an existing subject.

Figure 5-10 - BT - Forum - New Subject
The creation of a new subject is defined by the creation of a new Asset. It can be done by the Forum Creator (FC) or an Editor (E). When a new subject is opened, the Publisher creates a new Asset (Sni) and sends one unit of the Asset to the Publication Wall. The transaction carries on the publication which can be read anyone able to connect to the BlockChain.
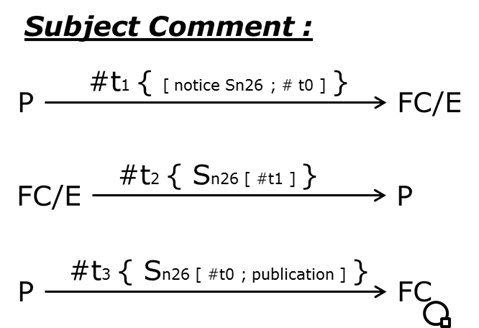
Figure 5-11 - BT - Forum - Comment
The Creator of an Asset is the owner of this Asset. He is then the only one able to create new units of the Asset.
In the Forum use case, the interest is to track Subjects and comments on the Subjects. For that, the same Assets are used to create the subject and comment it. To comment a publication, people need to ask one unit of the Asset to the Creator of the publication.
Someone (P) who wants to comment create a transaction only with data. The data indicates what is the Subject to be commented is and what is the transaction to be commented. The transaction is sent to the address of the Creator of the Subject (FC/E).
If the Creator of the Subject decides to allow the comment, then he sends to (P) one unit of the Asset referencing the transaction used to ask this unit.
At the end, (P) can send his comment to the Publication Wall using the unit of Asset, referencing the transaction to comment and giving his comment.